In clinical use for a quarter of a century (Roulet 1989 Theiss 2009)
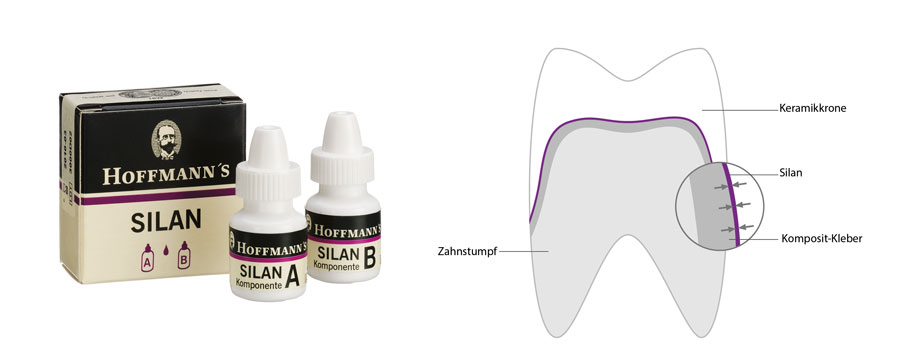
- To increase the chemical bonding force during adhesive cementation of silicate ceramics, silicated oxide ceramic or metal restorations with methacrylate bearing cementation materials (composites, compomers and ormocers)
- As a ceramic-composite bonding agent for ceramic repairs
Benefits of Hoffmann’s two-component silane
- Full reaction force as the reagents are mixed freshly before each use
- Longer shelf life after opening the bottle
- Optimal chemical bonding surface with simultaneous good surface wettability
- Prevention of adhesion defects
HOW IT WORKS
The reagents A and B of Hoffmann’s silane are mixed 1:1, which creates silanol, the reactive agent. Silicate-based ceramics, such as leucite glass ceramic (IPS Empress) and fluoroapatite-ceramic (IPS-e. Max ZirPress) are first etched with hydrofluoric acid to form a micro-retentive, crystalline surface structure.
During silanization of the silica surface, a chemical bond between silanol and ceramic is formed through the reaction of the methoxy group of the silanol with the silicon oxide group of the ceramic with the formation of Si-O-bridges.
The short hydrocarbon rests of the silanols have a reactive double bond, which can then polymerize onto the adhesive composite.
| SILANE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Order No. | Package size | Colour | Composition |
| 82101 | Component A, 5 ml Component B, 5 ml |
— | Acetic acid in ethanol solution, 3-methacryloyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane in ethanol solution |
Download

